2D Echo GLS
Global longitudinal strain ( GLS) : Fine-tuning your 2D echo
Heart pumping i.e. left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ( function of heart muscle) is considered an important predictor of long-term outcomes in a variety of problems. However, recent scientific advances have shown a new insight that LVEF is affected later in course of the disease. Global longitudinal strain is more sensitive than ejection fraction and it can detect changes in heart muscle at a very early stage. Even if the ejection fraction is normal, abnormal GLS signifies advanced disease.
How GLS is done:
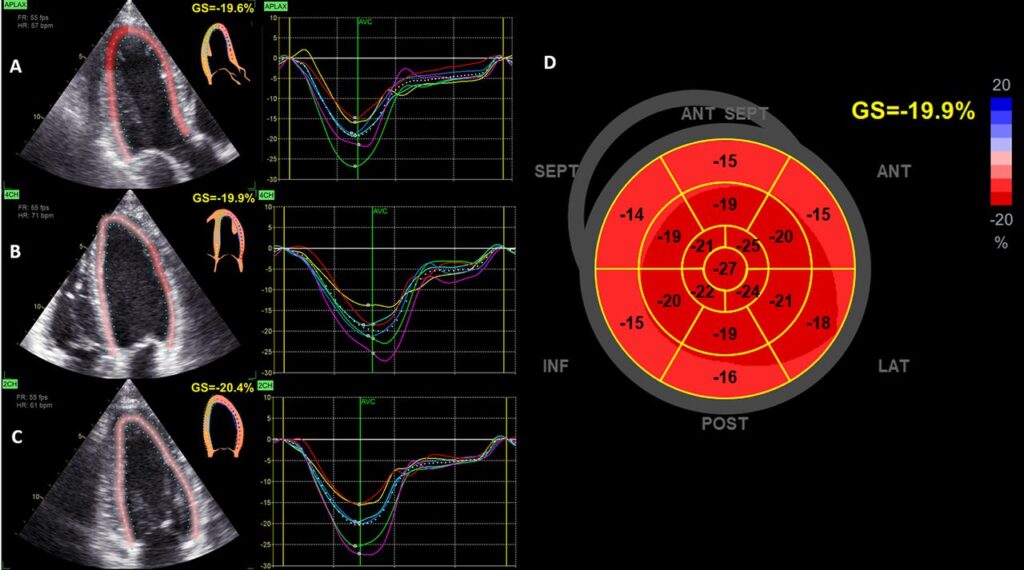
GLS is a type of advanced echocardiography where imaging of heart muscle is done in a more precise manner. It quantifies the shortening of every segment of the left ventricular muscle. Integrating all segments, a bull’s eye image is created as shown below. It gives local as well as global longitudinal stains.
A disease where GLS can be useful:
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Elderly with diabetes and hypertension have this condition.
- Post Covid myocarditis – Inflammation and damage of heart muscle cells by Covid-19 viral infection.
- Ischemic heart disease in a stable person
- Left ventricular hypertrophy: Athlete’s heart, hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, amyloidosis
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Unstable angina: ( A type of heart attack) for early diagnosis
- Valvular heart disease: severe aortic stenosis/ aortic regurgitation, mitral regurgitation, etc
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Myocarditis: inflammation of the heart
- Systemic inflammation: systemic sclerosis,
- Post-cancer chemotherapy: Chemotherapeutic agents have an adverse effect on cardiac function. GLS is a well-established marker in this condition.
GLS Can Predict heart failure in stable person
Frequent Searches
GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Nanded City | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Pune | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre Nanded City, Pune | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre| GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre Near Me | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Sinhgad Road | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Dhayari | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Shivane | GLS 2D Echo Sonography cost in Pune | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Price in Pune | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Narhe | GLS 2D Echo Sonography Centre in Warje
Our Work Areas
Nanded City Pune | Sinhgad Road | Shivane | Dhayari | Narhe | Khadakwasla | Kothrud |
UttamNagar | Warje | Donje | DSK Vishva |DSK | Katraj
